What is dental trauma?
Dental trauma includes a variety of injuries to the teeth and oral tissues. The most common reasons include:
- Accidents: Serious dental damage can result from falls or collisions, especially in children.
- Sports damages: Impacts and falls in contact sports such as football and hockey often cause mouth injuries.
- Falls: Teeth can split, break, or become completely loose as a result of steep falls.
Dental trauma can take different forms, including:
- Chipped Tooth: When a small part of the tooth breaks off, leading to discomfort or sensitivity.
- Dislocated Tooth (Avulsed Tooth): This occurs when a tooth is completely knocked out of its socket.
- Fractured Tooth: A fractured tooth is one that has a crack or break, which may differ in severity.
- Soft Tissue Injuries: These injuries cause bruising or rips in the gums or other soft tissues of the mouth.
Understanding the types and causes of dental trauma is key to proper treatment and management.

How to manage dental trauma?
It’s critical to intervene quickly when oral trauma occurs. Here is a detailed guide on how to properly treat dental trauma:
Handling a knocked-out tooth
If a tooth has been knocked out, follow these steps:
- Find the Tooth: Use only the crown (the top portion) to locate the tooth but keep in mind not to come into contact with the root.
- Rinse: If the tooth is dirty, gently rinse it with milk or saline solution. Avoid using soap or scrubbers.
- Reinsert if Possible: If you can, gently place the tooth back into its socket. In order to secure it, have the individual bite down on a sanitized cloth.
- Preserve the Tooth: If reinsertion isn’t possible, store the tooth in a container with milk or saline solution to keep it damp.
Read More: Empowering Quotes for Complex PTSD
Managing a fractured or chipped tooth
If your tooth is chipped or broken, take the following actions:
- Rinse: Gently rinse your mouth with warm water to clean the area.
- Control Bleeding: Use a clean towel to gently press on any bleeding that develops.
- Pain Management: Until you can visit a physician, use over-the-counter pain medicines to assist control your suffering.
Dealing with soft tissue injuries
For injuries to the gums or other soft tissues:
- Rinse: Wash your mouth out with warm salt water.
- Apply Pressure: If there’s bleeding, apply gentle pressure with a clean gauze or cloth.
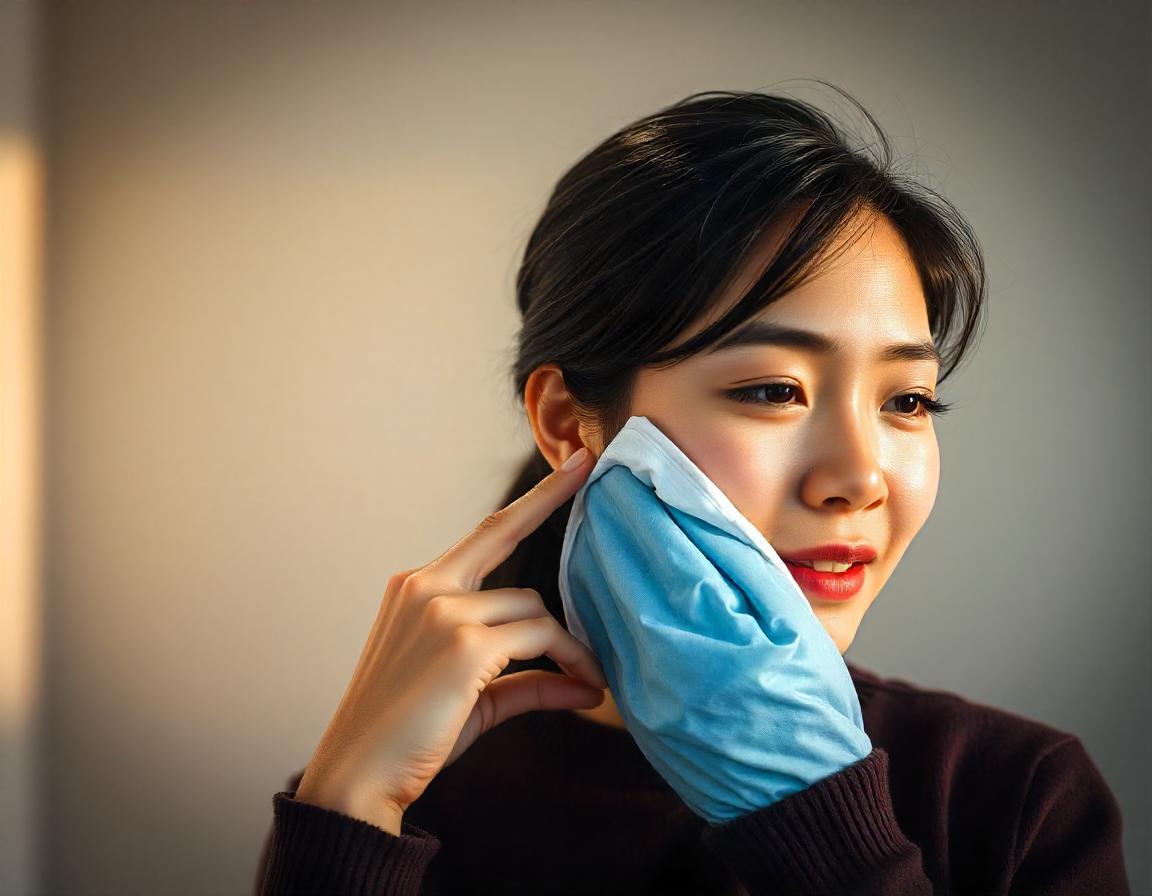
- Cold Compress: Use a cold compress on the outside of the mouth to reduce swelling.
Emergency Dental Trauma First Aid
In cases of dental trauma, prompt action is essential. Here’s a first-aid checklist for emergency dental trauma:
- Stop Any Bleeding: If there’s bleeding, apply pressure to the area using a clean cloth.
- Preserve a Knocked-Out Tooth: Store the tooth in milk or saline solution if it cannot be reinserted.
- Control Swelling: Apply a cold compress to the area in question to reduce discomfort and swelling.
- Pain Management: Take over-the-counter pain relievers to help manage any pain.
These emergency dental trauma first aid procedures can greatly increase the likelihood that your treatment may be successful.
When to seek professional dental help
It’s critical to identify severe dental injuries that require emergency care. Keep an eye out for:
- Severe Pain: Persistent pain that doesn’t lessen with over-the-counter medication.
- Excessive Bleeding: Bleeding that continues for more than 10 minutes, even with applied pressure.
- Visible Tooth Displacement: Teeth that seem loose or misaligned.
- Signs of Infection: Swelling, redness, or pus around the injured area.
If you notice any of these signs, seek professional dental care immediately.
In conclusion, the outcome can be significantly impacted by understanding how to treat dental injuries appropriately and administering first aid right away. You and your family will be more equipped to handle dental emergencies if you abide by the dental trauma guidelines in this article.Keep your emergency dental contact information close at hand and be informed on the most current research regarding the treatment of possible dental traumas.
FAQ section
What should I do if my child knocks out a tooth?
If your child loses a tooth, rinse it gently and try to reinsert it into the socket. If that’s not possible, place the tooth in milk or saline solution and seek immediate dental care.
How can I prevent dental trauma in sports?
Using a mouthguard during contact sports can greatly reduce the risk of dental injuries.
When should I see a dentist after dental trauma?
You should see a dentist if there is severe pain, heavy bleeding, tooth misalignment, or signs of infection.
Are there home remedies for dental trauma pain?
You can alleviate pain and swelling from dental trauma using over-the-counter pain relievers, applying cold compresses, and rinsing with warm saltwater.
What happens if a knocked-out tooth isn’t treated right away?
Delaying treatment reduces the chances of successfully saving the tooth and can lead to complications, such as infection or damage to adjacent teeth.