In this article, we will explore the core aspects of trauma and orthopaedics, delving into common conditions, treatment options, and rehabilitation strategies. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how the field of trauma and orthopaedics supports healing and recovery.
What are trauma and orthopaedics?
Trauma refers to injuries caused by external forces, such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries. These injuries can range from minor fractures to life-threatening conditions like traumatic spinal injuries. Orthopaedics, on the other hand, focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders related to the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments.
When combined, trauma and orthopaedics form a critical branch of medicine that deals with acute injuries as well as chronic conditions affecting movement and mobility. Trauma and orthopaedic surgeons often work in emergency settings, performing procedures to fix broken bones, joint dislocations, and other musculoskeletal trauma.
Common trauma and orthopaedic conditions
The field of trauma and orthopaedics covers a wide array of conditions. Here are some of the most common:
1. Fractures
A fracture occurs when a bone is broken due to a sudden force. Fractures can range from simple breaks that only need immobilization to complex fractures requiring surgery. Open (compound) fractures, where the bone pierces the skin, need immediate medical attention to prevent infection.
Treatment: Immobilization with casts, splints, or braces is common for simple fractures. For severe cases, orthopaedic surgeons may need to use metal rods, plates, or screws to realign and stabilize the bone.
2. Joint dislocations
A dislocation happens when the bones in a joint are forced out of their natural alignment, typically due to a sudden trauma or injury. Commonly dislocated joints include shoulders, knees, elbows, and fingers.
Treatment: Orthopaedic surgeons manually reposition the bones (reduction), followed by immobilization with a sling or brace. In recurrent cases, surgery might be required to repair or tighten the supporting ligaments.
3. Arthritis
Arthritis is a chronic condition that causes inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. There are several types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis being the most common. It occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of bones wears down over time.
Treatment: Non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications are often recommended. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary. Online therapy can also be beneficial for managing the psychological aspects of living with arthritis.
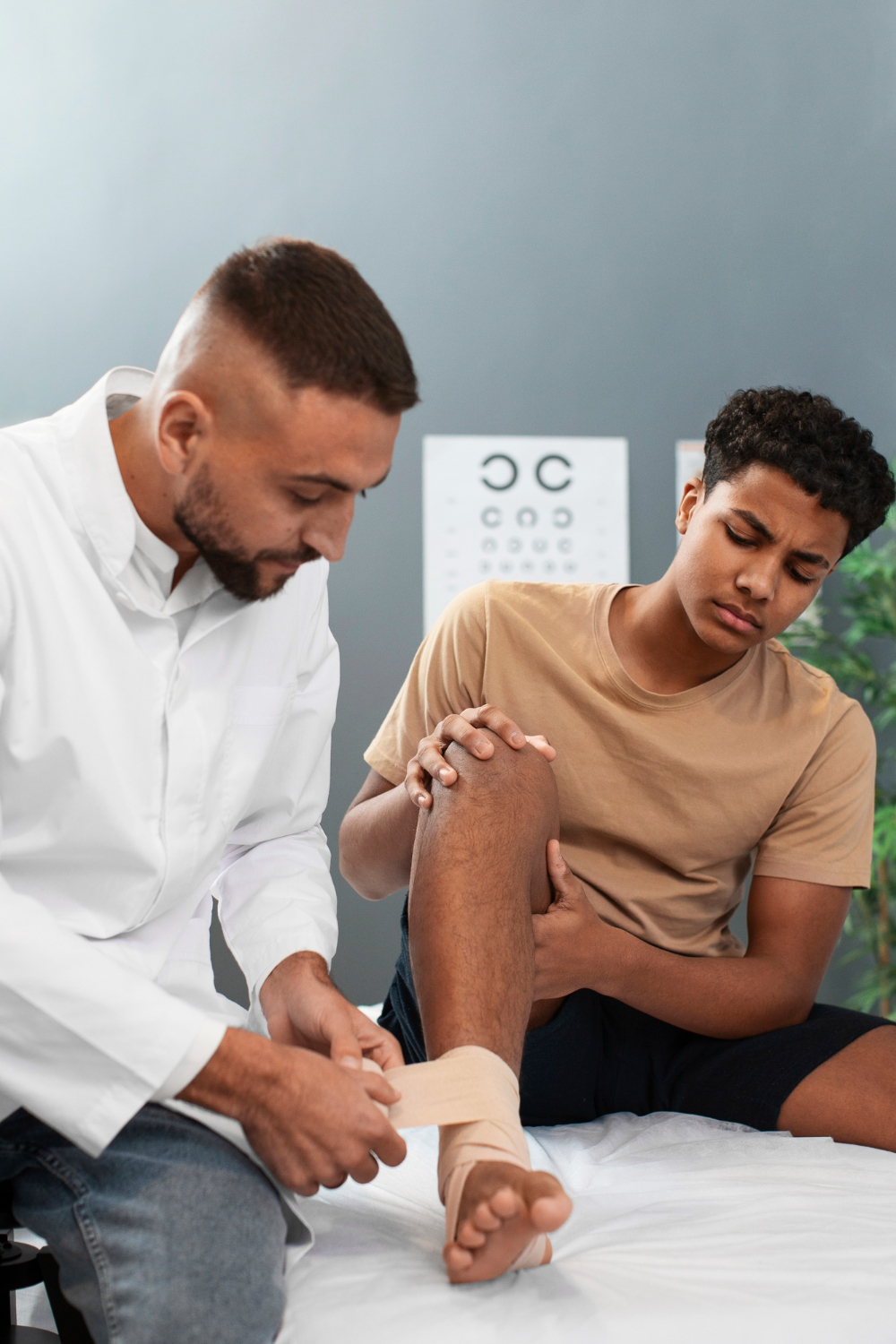

4. Ligament and Tendon Injuries
Injuries to ligaments and tendons often occur during sports activities or sudden movements. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee is particularly prone to injury, especially in athletes.
Treatment: Depending on the severity, treatment can range from rest and physical therapy to surgical repair or reconstruction, particularly for torn ligaments like the ACL. Online therapy may help athletes cope with the emotional challenges of recovery.
5. Spinal injuries
Spinal trauma can result from accidents or falls, and injuries to the spine can have long-lasting consequences. Conditions such as herniated discs, fractures, or spinal cord injuries may require surgical intervention.
Treatment: Treatments vary depending on the injury but may involve surgery, spinal fusion, or non-surgical approaches like physical therapy, medications, and spinal braces. Additionally, online therapy can provide support for managing pain and adjusting to lifestyle changes after a spinal injury.
Read More: Empowering Quotes for Complex PTSD
Treatment options in trauma and orthopaedics
The approach to treating trauma and orthopaedic conditions depends on the type and severity of the injury. Some of the common treatment methods include:
1. Non-surgical treatments
Non-surgical approaches are often the first line of treatment, especially for mild to moderate injuries. These may include:
- Physical Therapy: Helps to restore movement and strength.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs help manage pain and swelling.
- Braces, Splints, and Casts: Provide support and stability to healing bones and joints.
2. Surgical treatments
When non-surgical methods are insufficient or when injuries are severe, surgery may be necessary. Common orthopaedic surgeries include:
Fracture Fixation: Using rods, screws, or plates to hold broken bones in place.
- Joint Replacement: Replacing a damaged joint with an artificial one, commonly performed on the hip or knee.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows doctors to look inside the joint and treat issues such as torn cartilage or ligaments.
- Spinal Surgery: Procedures like spinal fusion or discectomy are used to treat severe back injuries or degenerative disc disease.

Rehabilitation and recovery in trauma and orthopaedics
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in the recovery process following a trauma or orthopaedic injury. It aims to restore function, improve mobility, and reduce pain, helping patients regain their quality of life.
1. Physical therapy
Physical therapy is an essential component of rehabilitation, especially after surgery. Therapists design tailored programs that involve exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance balance.
2. Occupational therapy
In cases where daily activities are affected, occupational therapy focuses on helping patients regain the ability to perform routine tasks, such as dressing, bathing, or cooking.
3. Pain management
Pain can linger after an injury or surgery, so effective pain management is crucial. This may involve medications, nerve blocks, or alternative therapies like acupuncture.
4. Lifestyle modifications
In chronic conditions like arthritis, lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. This may include weight management, regular exercise, and dietary adjustments to reduce inflammation.
The role of trauma and orthopaedic surgeons
Trauma and orthopaedic surgeons are highly trained specialists who handle both emergency and planned procedures. Their expertise extends beyond treating acute injuries to managing chronic conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. These surgeons often collaborate with other healthcare professionals such as physiotherapists, pain specialists, and occupational therapists to ensure comprehensive care for their patients.
Surgeons in this field undergo extensive training in medical school, followed by years of specialised training in trauma and orthopaedic surgery. Many also choose to specialise further in areas like sports injuries, spinal surgery, or joint replacements.
The importance of trauma and orthopaedics in recovery and well-being
Trauma and orthopaedics play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and rehabilitating injuries and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. From fractures and joint dislocations to chronic conditions like arthritis, the expertise of trauma and orthopaedic specialists ensures patients receive the appropriate care for their unique needs. Whether through non-surgical treatments, advanced surgical interventions, or comprehensive rehabilitation, the goal is always to restore mobility, alleviate pain, and improve overall quality of life. With the right medical support, patients can regain their strength and confidently return to daily activities.